Ozempic has suddenly become one of the most talked-about health solutions in the world. Some people praise it for dramatic weight loss. Others take it to control type 2 diabetes. And many are confused about one simple question:
How can one weekly injection affect hunger, blood sugar, and body weight at the same time?
If you are curious but overwhelmed by medical terms, you are not alone. This article explains how Ozempic works inside the body in the simplest possible way, without complex science or confusing language.
By the end of this guide, you will clearly understand why Ozempic reduces appetite, improves blood sugar control, and leads to weight loss for many people.
What Exactly Is Ozempic?
Ozempic is a prescription medication originally developed to help people with type 2 diabetes manage their blood sugar levels. It is taken as a once-weekly injection.
However, during treatment, doctors noticed something unexpected.
Many patients started losing weight naturally, even without strict dieting.
This unexpected benefit turned Ozempic into a trending health topic worldwide.
You may also like : Ozempic 101: A Complete Guide to This Trending Health Solution
The One Hormone That Explains Everything: GLP-1
To understand Ozempic, you only need to know one hormone.
That hormone is called GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1).
Your body naturally releases GLP-1 after you eat. This hormone sends important signals that help your body manage food and sugar.
GLP-1 tells your body:
- You are full
- Slow down digestion
- Control blood sugar
Ozempic copies this natural hormone, but in a stronger and longer-lasting form.
That is the real secret behind how it works.
How Ozempic Works for Diabetes (Step by Step)
Ozempic helps people with type 2 diabetes in three main ways.
1. It Helps the Body Release Insulin at the Right Time
Insulin moves sugar from your blood into your cells for energy. In diabetes, this process does not work properly.
Ozempic helps by:
- Increasing insulin only when blood sugar is high
- Avoiding unnecessary insulin release when sugar is normal
This balance improves blood sugar control and lowers the risk of sudden sugar crashes.
2. It Stops the Liver From Releasing Extra Sugar
Your liver stores sugar and releases it when needed. In people with diabetes, the liver often releases too much sugar, even when it is not required.
Ozempic sends a signal to the liver to:
- Reduce unnecessary sugar release
- Keep blood sugar more stable throughout the day
This helps prevent high fasting blood sugar levels.
3. It Slows Down Digestion
Ozempic slows how fast food leaves your stomach.
This means:
- Sugar enters the bloodstream slowly
- Blood sugar spikes after meals are reduced
For people with diabetes, this gentle slowing effect makes a big difference.
How Ozempic Works for Weight Loss (The Real Reason)
Now let’s talk about weight loss, the reason Ozempic became so popular.
Ozempic does not burn fat directly.
Instead, it changes how hunger works.
1. It Quietly Reduces Hunger Signals
Ozempic acts on the appetite control center of the brain.
Many people notice:
- Feeling full very quickly
- Less interest in food
- Reduced cravings, especially for sugar and junk food
You are not forcing yourself to eat less.
You simply do not feel the same hunger.
2. Fullness Lasts Much Longer
Because digestion is slower:
- Food stays in the stomach longer
- Fullness lasts for hours
This naturally leads to:
- Smaller portion sizes
- Fewer snacks
- Lower calorie intake without effort
3. Emotional and Mindless Eating Reduces
Many users say Ozempic changes their relationship with food.
Things like:
- Stress eating
- Late-night snacking
- Constant food thoughts
often reduce significantly.
This mental shift is one reason weight loss feels easier for many people.
What Ozempic Is Doing Inside the Body (Visual Overview)


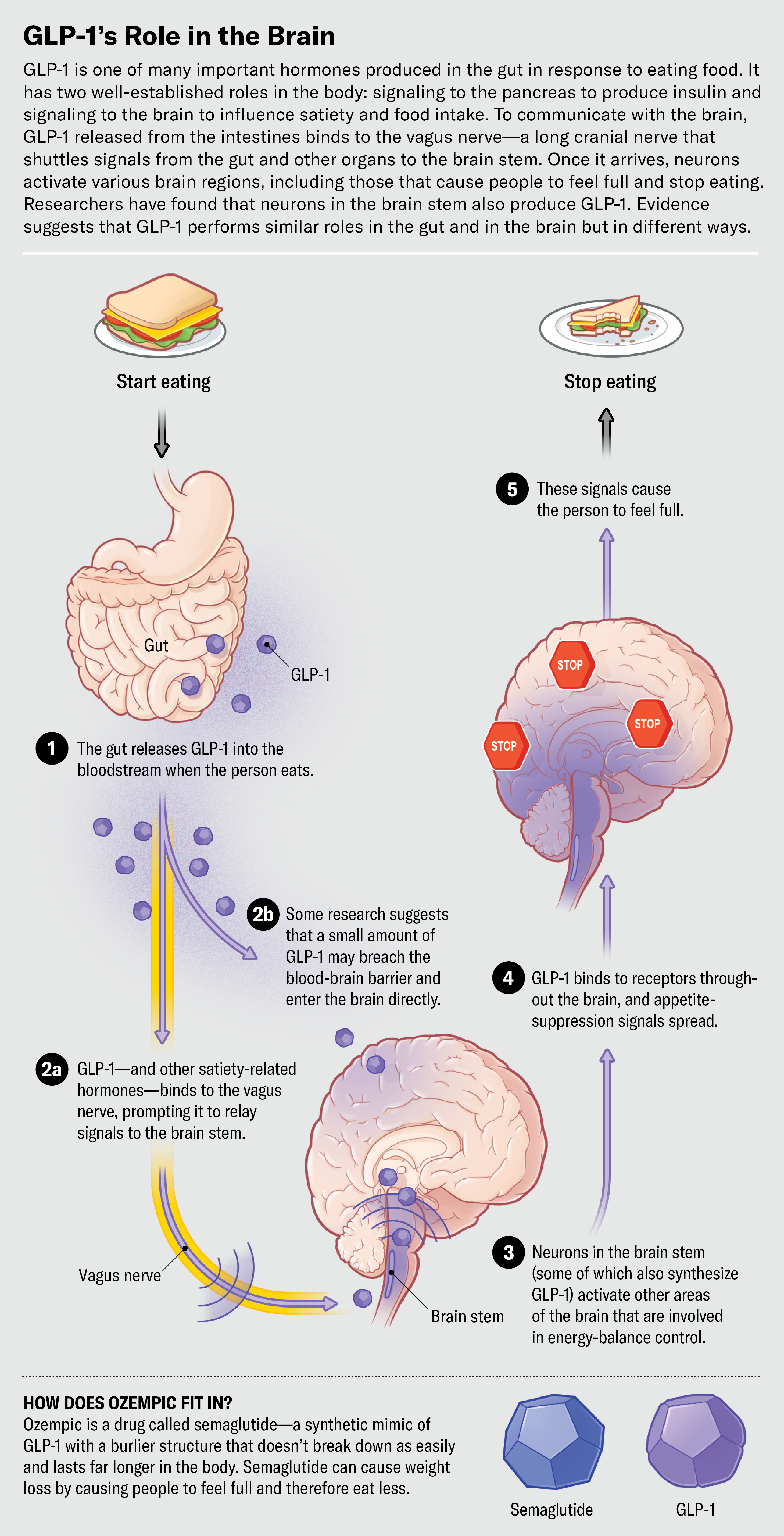
In simple terms, Ozempic:
- Reduces hunger
- Slows digestion
- Improves blood sugar balance
That combination affects both diabetes and weight at the same time.
Why Weight Loss on Ozempic Feels Different
Traditional weight loss depends heavily on:
- Strong willpower
- Strict diets
- Constant hunger
Ozempic works on biology, not motivation.
That is why many people say:
- “I stop eating naturally”
- “I feel satisfied with less food”
- “Food doesn’t control my thoughts anymore”
This does not mean Ozempic is magic.
It means hunger is no longer fighting against you all day.
How Fast Does Ozempic Start Working?
Most people notice changes gradually.
- First 1–2 weeks: Appetite starts reducing
- Weeks 3–6: Clear reduction in food intake
- 2–3 months: Visible weight loss and better sugar control
- 6 months and beyond: Significant improvement for many users
Results vary based on dosage, lifestyle, and individual body response.
Does Ozempic Work Without Diet or Exercise?
Ozempic can still help with weight loss even without strict dieting. However, results are better and more stable when combined with:
- Balanced meals
- Enough protein
- Light physical activity
Ozempic is a support tool, not a replacement for healthy habits.
A Common Misunderstanding About Ozempic
Ozempic:
- Does not melt fat
- Does not instantly boost metabolism
- Does not work overnight
Weight loss happens because you eat less naturally, not because fat disappears magically.
What Happens When Ozempic Is Stopped?
When Ozempic is stopped:
- Hunger often returns
- Old eating patterns may come back
- Weight regain is possible
This is why doctors encourage:
- Long-term habit changes
- Gradual transitions
- Medical supervision
Final Thoughts: Why Ozempic Works So Well for Some People
Ozempic targets the root causes behind weight gain and high blood sugar:
- Excess hunger
- Poor appetite control
- Blood sugar imbalance
Instead of forcing discipline, it helps the body self-regulate.
For many people, this feels life-changing.
For others, it may not be suitable.
That is why proper medical guidance always matters.
Important Note
This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting or stopping any medication.

